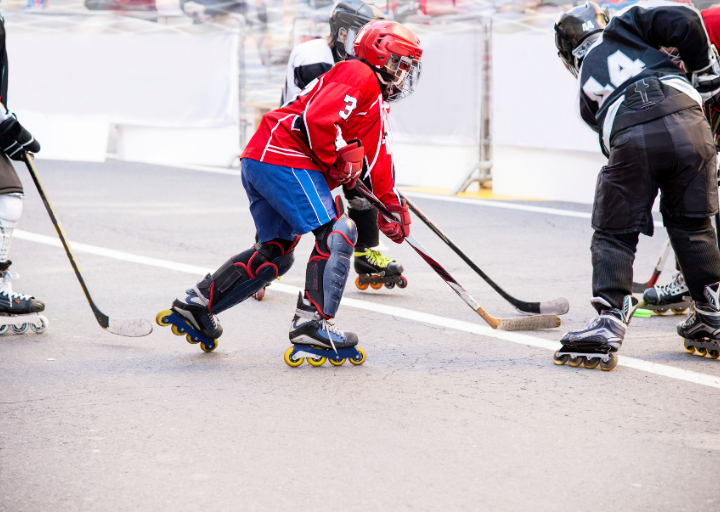
Youth hockey is a thrilling sport that offers numerous physical and social benefits to young athletes. However, like any contact sport, it comes with inherent risks, particularly when it comes to injuries. To ensure the safety and well-being of young hockey players, it is crucial to implement effective injury prevention strategies. In this comprehensive review, we will explore the best practices in youth hockey injury prevention, examining various aspects of the game and strategies to minimize the risk of injuries.
Understanding the Risk Factors
Before delving into specific prevention strategies, it is essential to understand the risk factors associated with youth hockey injuries. Recognizing these factors can help tailor prevention efforts more effectively.
1. Age and Development Stage
Youth hockey encompasses a wide age range, from early childhood to adolescence. It’s important to consider the developmental stage of players, as their physical growth and skill level can significantly affect injury susceptibility.
2. Playing Level and Competition
The level of competition varies widely in youth hockey, from recreational leagues to highly competitive travel teams. The intensity and competitiveness of play can influence injury risk.
3. Gender Differences
Recognizing gender-specific injury patterns and risk factors is pivotal in tailoring injury prevention strategies for male and female youth hockey players. Research reveals nuanced differences that impact injury susceptibility, and addressing these distinctions can lead to more targeted and effective safety measures, ultimately enhancing the well-being of all participants in the sport.
Proper Equipment and Safety Gear
One of the foundational elements of youth hockey injury prevention is ensuring that players have access to and wear the appropriate safety equipment.
1. Helmets
Helmets are the most critical piece of protective gear in hockey. They should meet the required safety standards and be regularly inspected for damage. Properly fitted helmets can reduce the risk of head injuries.
2. Face Shields and Cages
Full-face shields or cages attached to helmets are essential for protecting players’ faces from injuries, particularly in youth leagues where high-sticking incidents are more common.
3. Mouthguards
Mouthguards are crucial for protecting against dental and orofacial injuries. Ensuring all players wear properly fitted mouthguards is vital.
4. Neck Guards
Neck guards provide added protection against lacerations and other neck-related injuries. They should be mandatory in youth hockey.
5. Shoulder Pads, Elbow Pads, and Shin Guards
These protective gear pieces should fit well and offer sufficient padding to absorb impacts and reduce the risk of fractures and soft tissue injuries.
Training and Conditioning
Youth hockey players should undergo appropriate training and conditioning to prepare their bodies for the physical demands of the sport.
1. Strength and Conditioning Programs
Implementing age-appropriate strength and conditioning programs can help players build muscle strength and endurance, reducing the risk of injuries.
2. Skating and Balance Training
Skating is a fundamental skill in hockey. Skating and balance training can enhance agility and stability on the ice, reducing the risk of falls and related injuries.
3. Proper Warm-Up and Stretching
Before every practice or game, players should engage in a thorough warm-up routine and stretch to prevent muscle strains and injuries.
Rule Modifications and Enforcement
Youth hockey leagues can implement rule modifications to reduce dangerous plays and injuries.
1. Checking Rules
Adjusting checking rules based on age and skill level can minimize the risk of body checking-related injuries, especially in younger players.
2. Penalties for Dangerous Play
Enforcing strict penalties for dangerous plays, such as high-sticking or slashing, can deter risky behavior on the ice.
3. Coaches’ Education
Educating coaches about the importance of fair play and sportsmanship can help create a safer environment for youth hockey.
Safe Playing Environments
The rink and playing environment play a significant role in injury prevention.
1. Ice Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the ice surface is essential to minimize uneven areas that can lead to falls and injuries.
2. Proper Board Padding
Well-padded rink boards can reduce the impact of collisions with the boards, decreasing the risk of injuries.
3. Goalie Safety
Goalies are particularly vulnerable to injuries. Ensuring they have proper protective gear and receive specialized training is crucial.
Concussion Awareness and Management
Concussions are a significant concern in hockey. It’s essential to raise awareness and implement proper management protocols.
1. Education
Players, coaches, and parents should be educated about the signs and symptoms of concussions to ensure early detection and treatment.
Education is paramount in the prevention and management of concussions. Players, coaches, and parents must familiarize themselves with the signs and symptoms of concussions, such as headaches, dizziness, memory problems, and mood changes. This knowledge enables early detection, allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of further damage.
2. Baseline Testing
Implementing baseline testing for players can aid in diagnosing concussions and determining when it’s safe for a player to return to play.
Baseline tests include neurocognitive assessments, balance evaluations, and symptom tracking, providing a comprehensive profile of a player’s abilities. These assessments not only assist in diagnosis but also guide the return-to-play decision-making process. By ensuring that a player’s cognitive and physical functions have fully recovered to baseline levels, we minimize the risk of returning to play prematurely, protecting athletes from potential long-term consequences.
3. Return-to-Play Protocols
Strict return-to-play protocols should be followed to ensure that players do not return to the ice prematurely after a concussion.
Strict return-to-play protocols are crucial to safeguard the long-term health and well-being of athletes in contact sports like ice hockey. Concussions, though often considered minor injuries, can have lasting consequences if not managed properly. These protocols, devised by medical experts and sports organizations, involve a gradual and systematic approach to evaluate a player’s readiness to rejoin the ice.
Injury Surveillance and Reporting
A robust system for injury surveillance and reporting is essential for understanding injury trends and developing targeted prevention strategies.
1. Injury Logs
Maintaining comprehensive hockey injury logs is an indispensable tool in safeguarding the well-being of young athletes. These logs serve as a treasure trove of data that, when properly analyzed, can guide evidence-based injury prevention strategies.
By recording the types and frequencies of injuries, we gain valuable insights into injury patterns specific to youth hockey. Are concussions more common than sprained ankles? Do certain positions or age groups face higher risks? Such data can pinpoint where prevention efforts should be concentrated.
2. Reporting Mechanisms
Establishing clear and efficient mechanisms for reporting injuries can ensure that incidents are documented and analyzed promptly.
Efficient reporting systems encourage athletes, coaches, and medical staff to share critical injury information. This allows for the early identification of injury trends and risk factors. It also ensures that injured players receive timely medical attention, preventing aggravation of injuries.
Parent and Player Education
Parents and players themselves play a critical role in injury prevention. Here is how:
1. Proper Hydration and Nutrition
Hydration is a critical component of athletic success, and it’s especially vital in a high-intensity sport like hockey. When players are well-hydrated, they can maintain their performance levels, stay mentally sharp, and reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion or heat stroke. Therefore, educating players and parents about the importance of hydration and nutrition can enhance player endurance and recovery.
2. Rest and Recovery
Teaching young athletes about the importance of rest and recovery is paramount in safeguarding their long-term health and athletic potential. Overuse injuries, such as stress fractures, tendonitis, and muscle strains, often arise when young athletes push themselves too hard without allowing their bodies adequate time to recover.
3. Encouraging Sportsmanship
Promoting sportsmanship and respect for opponents can reduce aggressive behavior and the risk of injuries stemming from dangerous plays. Teaching young athletes how to resolve conflicts peacefully and respectfully on the ice can prevent aggressive confrontations. Encouraging them to communicate and collaborate with opponents rather than resorting to physical aggression is key.
Conclusion
Youth hockey injury prevention is a multifaceted endeavor that requires the collaboration of players, coaches, parents, and league organizers. By understanding the risk factors, providing proper equipment, emphasizing training and conditioning, modifying rules, ensuring safe playing environments, addressing concussions, and promoting injury surveillance and education, we can create a safer and more enjoyable environment for young hockey players. It is crucial that these best practices are consistently implemented to protect the well-being of our youth athletes and allow them to thrive in this exciting sport.