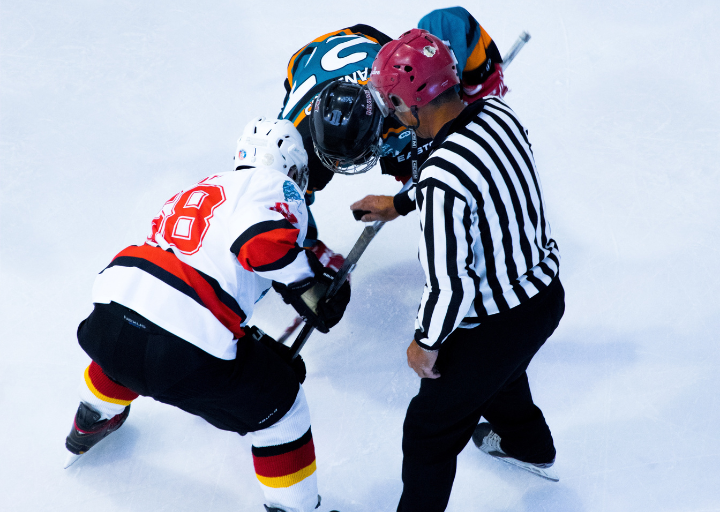
Muscle strains stand as a prevalent concern within the dynamic and physically demanding realm of hockey. This high-speed, contact sport places rigorous demands on the musculoskeletal system, often leading to muscle strains, which are among the most common injuries faced by players. Hockey’s combination of explosive skating, sudden changes in direction, forceful shooting, and physical contact creates an environment where muscles are susceptible to overexertion and strain.
Hockey muscle strains, characterized by the stretching or tearing of muscle fibers, can significantly impact a player’s performance and overall well-being. The rapid acceleration and deceleration required during gameplay, coupled with the intensity of competition, make players vulnerable to these injuries. Understanding the risk factors and adopting preventative strategies is paramount in fostering player longevity and minimizing time spent on the sidelines.
In this context, this article delves into the intricate interplay between muscle strains and hockey. We explore the underlying causes of muscle strains, the specific muscles most susceptible, and the common scenarios in which these injuries tend to occur.
Take a look!
Tips to Prevent Muscle Strains in Hockey
Muscle strains are a common concern in the world of hockey, where intense physical demands and quick movements can put significant stress on the body. To ensure you’re playing at your best while reducing the risk of muscle strains, it’s essential to adopt a proactive approach to injury prevention.
Warm Up and Stretching: Setting the Foundation
Start your preparation with a thorough warm-up session. This should include light aerobic exercises and dynamic stretches that mimic the movements you’ll perform during the game. By gradually increasing your heart rate and blood flow, you prepare your muscles for the challenges ahead. Focus on the major muscle groups used in hockey, such as the hamstrings, quadriceps, calves, and hip flexors, as these areas are particularly susceptible to strains.
Strength and Conditioning: Building Resilient Muscles
Building strength through a well-rounded conditioning program is a key aspect of preventing muscle strains. Develop a comprehensive routine that targets your core, legs, and upper body. Functional exercises that mirror the demands of hockey, such as squats, lunges, and resistance training, can help you develop the necessary stability to reduce the risk of overuse hockey injuries.
Proper Technique: Playing Smart and Safe
Learning and practicing proper technique is not only crucial for excelling in hockey but also for preventing muscle strains. Use correct body mechanics while skating, shooting, and checking to avoid placing unnecessary strain on your muscles. Prioritize good form to prevent muscle imbalances that can lead to strains over time.
Rest and Recovery: Finding the Balance
Finding the right balance between activity and rest is essential for preventing injuries like muscle strains. Give your body sufficient time to recover between intense practices and games. Overtraining can lead to fatigue and increase the risk of injuries, including strains. Prioritize quality sleep, hydration, and proper nutrition to support your body’s recovery process.
Protective Gear: Safeguarding Against Impact
Incorporating well-fitted protective gear is essential to safeguarding against direct impacts that could lead to muscle strains. Helmets, shoulder pads, and shin guards provide crucial protection. By reducing the impact of collisions, you can minimize the risk of muscle strains caused by sudden jolts or impacts during play.
Cross-Training: Diversifying Your Workout Routine
Engaging in a variety of physical activities beyond hockey is an effective way to prevent muscle imbalances and overuse injuries. Cross-training not only enhances your overall fitness but also helps develop different muscle groups. By varying your workout routine, you reduce the risk of strain from repetitive motions that are common in hockey.
Flexibility Maintenance: Stretching for Longevity
Incorporating regular stretching into your routine helps maintain muscle flexibility. This reduces the risk of tightness that can lead to strains. Consider activities like yoga or Pilates, which focus on flexibility and balance, to enhance your overall muscular health.
Cool Down and Recovery: Easing Out of Activity
After playing, take the time for a proper cool-down routine. Engage in light exercises and static stretches to gradually lower your heart rate and promote muscle recovery. This cool-down process supports relaxation and prevents post-activity muscle tension that could contribute to strains.
Listening to Your Body: Recognizing Warning Signs
Paying attention to your body’s signals is vital for preventing muscle strains. During play, be mindful of any signs of discomfort or fatigue. Address tightness or pain promptly to prevent the situation from worsening. Ignoring warning signs can lead to more serious injuries that might keep you sidelined for longer periods.
Professional Guidance: Seeking Expert Advice
When in doubt, don’t hesitate to seek advice from professionals in the field. Consult with a sports coach, athletic trainer, or physical therapist who specializes in injury prevention. These experts can provide personalized guidance and help create a tailored plan based on your individual needs and goals.
Effective Treatment for Muscle Strains in Hockey
Here are the effective treatments for muscle strains in hockey:
Rest and Protection
After experiencing a muscle strain during a hockey game, the initial step is to grant the injured muscle proper rest. Refrain from engaging in any activities that might worsen the strain. Employ protective measures such as compression wraps or braces to lend support and curtail swelling around the affected area.
Ice Therapy
In the immediate aftermath of the injury, applying ice becomes crucial. Ice therapy aids in mitigating pain and reducing inflammation. To execute this, gently place an ice pack on the affected area for intervals of 15-20 minutes, every 2-3 hours. Ensure that the ice pack is covered with a cloth to prevent direct contact with the skin.
Compression and Elevation
To manage swelling, employ compression bandages. These aid in maintaining control over the swelling and offer additional support to the injured muscle. When possible, elevate the injured area above the level of the heart. This elevation minimizes swelling and encourages improved blood circulation.
Pain Relief Medication
For the alleviation of pain and inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) available over-the-counter can be employed. However, it is prudent to consult a healthcare professional before using any medication, particularly if you possess allergies or pre-existing medical conditions.
Gradual Mobilization
As the initial pain and inflammation subside, initiate careful and controlled movement of the injured muscle. Introduce gentle range-of-motion exercises, aiding in the prevention of stiffness while fostering the healing process.
Physical Therapy
Enlisting the expertise of a physical therapist is highly recommended to facilitate proper rehabilitation. A personalized exercise regimen designed by a physical therapist aids in the gradual strengthening of the injured muscle, the restoration of flexibility, and the overall enhancement of muscle function.
Heat Therapy
After the initial acute phase, typically 48-72 hours post-injury, the application of heat can be beneficial. Heat therapy serves to relax the muscles and enhance blood circulation, promoting the healing process. Use warm packs or heating pads for short durations and exercise caution to avoid excessive heat and the risk of burns.
Ultrasound and Massage
Under the guidance of trained professionals, therapeutic techniques such as ultrasound and massage can prove effective. These practices contribute to improved blood flow, reduced formation of scar tissue, and the acceleration of healing in muscle strains.
Active Rest and Gentle Stretching
Continuing the recovery journey, consider engaging in light activities that do not strain the injured muscle. Gentle stretching routines aid in maintaining flexibility and guarding against muscle stiffness.
Gradual Return to Activity
Before re-engaging in full hockey activities, it is imperative to secure the approval of a medical professional. Begin reintroducing activities slowly, incrementally increasing intensity and duration as per the injured muscle’s tolerance.
Prevention Measures
Once fully recovered, direct your focus toward injury prevention strategies. Implement proper warm-up routines, adhere to regular stretching sessions, engage in strengthening exercises, and remain steadfast in maintaining correct technique. These proactive measures collectively serve to diminish the risk of future muscle strains.